| Panel
#3 – Color Dimensions
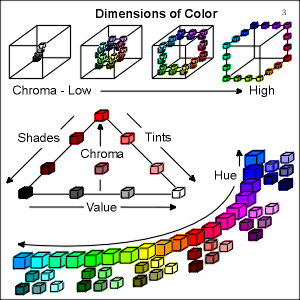
The basic dimensions of color are hue, value and chromaticity/saturation. Hue is the dimension of color that specifies a color’s position in the visible spectrum. Humans are able to interpret different combinations of red, green and blue and "see" the range of colors shown in the hue diagram. Tints and shades are variations of these pure hues and will be elaborated upon in panel #9. The value of a color refers to its lightness or darkness. White is the lightest color and therefore carries the highest value. Black carries the lowest value because it is the darkest color. In the COLORCUBE colors with "high value" are located near the white cube. In contrast, colors located near the black cube have "low value". Panel #4 discusses value in more depth. Chromaticity and saturation are often used interchangeably to describe how bright or vibrant a color is. The top diagram in panel #3 shows colors as they increase in chroma and approach the edge of the COLORCUBE. Shades of gray have no chroma and are called achromatic or monochromatic. Colors such as "fire engine red" and "canary yellow" are fully saturated and highly chromatic. |
|
Other Articles: Return to Articles Menu |